Diabetes
Diabetes is a condition where your blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is excessively high. Glucose serves as the primary energy source for your body. While your body can produce glucose, it is also obtained from the foods you consume.
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, facilitates the entry of glucose into your cells for energy utilization. In individuals with diabetes, the body either produces insufficient insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it makes. As a result, glucose remains in the bloodstream instead of being used by the cells.
The condition elevates the risk of harm to various parts of the body, including the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and heart. Diabetes has also been associated with an increased risk of certain cancers. Adopting measures to prevent or control diabetes can reduce the likelihood of experiencing complications related to the disease.
- Experiencing heightened thirst (known as polydipsia) and a persistently dry mouth.
- Urinating more often than usual.
- Feeling tired.
- Having a vision that is blurry or unclear.
- Losing weight without trying. Feeling numbness or a tingling sensation in the hands or feet.
- Noticing sores or cuts that heal very slowly.
- Experiencing recurrent skin and/or vaginal yeast infections.
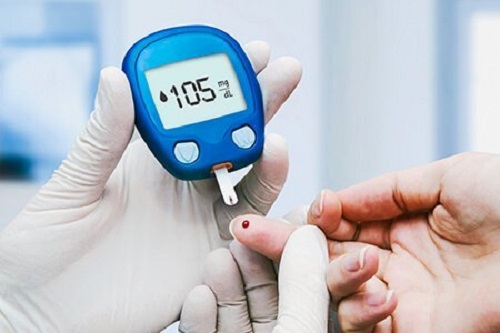
Monitoring Blood Sugar: Keeping an eye on your blood sugar (glucose) levels is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of your diabetes treatment plan. It helps you navigate daily management and make immediate adjustments as needed. You can track your glucose using regular tests with a glucose meter and finger pricks, or through a continuous glucose monitor (CGM). The ideal blood sugar range for you will be determined in consultation with your healthcare provider.
Oral Diabetes Medications: For individuals who still produce some insulin, particularly those with Type 2 diabetes and prediabetes, oral medications can play a significant role in controlling blood sugar levels. These medications are also sometimes prescribed for gestational diabetes. Metformin is among the most widely used of these drugs.
Insulin Therapy: Individuals with Type 1 diabetes must use synthetic insulin to survive and manage their condition. Some with Type 2 diabetes may need insulin as well. Various types of synthetic insulin are available, each with different onset times and durations of action. Insulin can be administered through injections with a syringe, insulin pens, pumps, or rapid-acting inhaled forms.
Dietary Management: Selecting a healthy diet and planning meals are central to controlling diabetes, as what you eat directly influences blood sugar levels. For those on insulin, carb counting is essential for determining insulin dosage at meals. Adopting healthy eating habits is also beneficial for weight management and reducing the risk of heart disease.
Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity boosts insulin sensitivity, making it a vital component of diabetes management for everyone with the condition.
